
Introduction
The insurance sector has traditionally relied on historical data, manual assessments, and rigid rule-based systems to evaluate risk and manage operations. According to the report of Deloitte, the insurance industry has grown to US$4.5 trillion in 2024, with a growth of 25%. However, the rapid rise of machine learning in insurance has fundamentally transformed the work structure of the insurance sector. This includes how insurers design products, price policies, detect fraud, and engage with customers. By leveraging advanced algorithms, backed up by data patterns, insurers can now make faster, more accurate, and more personalised decisions at scale.
From automating claims processing to improving customer service through intelligent chatbots, machine learning is no longer an optional innovation—it is a strategic necessity. This blog explores 5 key use cases of machine learning in insurance, explains how the industry has evolved, highlights major drawbacks, and concludes with insights into the future potential of this powerful technology.
Challenges Faced by Customers in Manual Insurance Processes
Before Machine learning integration, the manual insurance processes were troublesome in some cases, and that has actually impacted customer satisfaction. Someof the common issues faced were -
Long Processing and Approval Time
Before the adoption of machine learning in insurance, most insurance processes were manual. Customers had to wait days or even weeks for policy approvals, underwriting decisions, and claim settlements. Manual verification of documents, physical inspections, and multiple layers of approval slowed down the entire process. This has caused uncertainty for the customers, especially during urgent situations such as medical emergencies or accident-related claims.
Lack of Transparency and Poor Communication
The claim status and the underwriting process were less visible to the policyholders. Customers often had to rely on phone calls or branch visits to get updates, with no real-time tracking available. This lack of transparency created confusion and mistrust. They were unsure about the reasons for the delay and rejection, leading to a poor overall service experience.
Inconsistent Risk Assessment and Pricing
Without advanced analytics or Predictive modelling, insurers relied on human judgment and broad risk categories. Inconsistent underwriting and unfair pricing for the customers have been the common issues. Two individuals with similar profiles could receive different policy terms due to subjective decision-making. This made the customers think the policies were unreliable and biased.
High Error Rates in Claims and Documentation
Human errors such as missing information, incorrect policy details, or misplaced documents are common factors in manual paperwork. These errors often led to claim rejections or repeated requests for the same information. Customers had to resubmit documents multiple times, and this increased the waiting time and stress.
Limited Personalisation and Rigid Policies
Before personalised insurance models, policies were largely standardised and not flexible at all. Customers could not choose their insurance to suit their specific needs, health conditions, or lifestyles. This inflexible approach made the policies somewhat rigid, and sometimes customers had to pay for the coverage they did not even need.
Poor Customer Support Experience
Before chatbot automation and digital self-service tools were implemented, customer support was dependent on call centres with limited working hours andlimited agents. Long wait times, repeated explanations of issues, and inconsistent responses were very common. These factors negatively affected customer satisfaction and trust in insurers.
5 Use Cases of Machine Learning in Insurance
1. Anomaly and Fraud detection using Machine learning
Insurance fraud is one of the biggest challenges faced by insurers. This costs the industry billions every year. Machine learning in insurance plays a critical role in identifying suspicious behaviour by analysing large volumes of structured and unstructured data in real time.
Using anomaly detection machine learning, insurers can identify patterns that deviate from normal claim behaviour. For example, irrational or high claim amounts, repeated claims from the same individual, or inconsistencies between documents can be automatically flagged for investigation. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, anomaly detection models are trained continuously with new data. This makes them more effective against evolving fraud techniques.
Similarly, fraud detection using machine learning enables predictive analysis by training models on past fraud cases. These systems assign risk scores to claims, helping investigators prioritise high-risk cases and reduce false positives. As a result, insurers can minimise financial losses, speed up genuine claims, and improve overall trust in the insurance ecosystem.
2. Insurance Underwriting
Underwriting is the backbone of the insurance business, as it determines policy eligibility, pricing, and risk exposure. After the implementation of Machine learning in underwriting, the process has significantly improved in terms of accuracy and efficiency of this traditionally manual process.
Through underwriting using machine learning, insurers can combine historical policy data, customer demographics, behavioural data, and external datasets to assess risk more accurately. Predictive modelling techniques are widely used to forecast the likelihood of claims, helping insurers price policies more accurately.
Modern underwriting platforms, including Desktop Underwriter systems, use machine learning to automate decision-making while ensuring compliance with underwriting guidelines. These systems generate dynamic risk-scoring metrics, enabling underwriters to make faster and more consistent decisions.
By adopting machine learning, insurers reduce human bias, improve turnaround time, and offer more competitive policy pricing. These are done while maintaining profitability.
3. Automated Insurance Claims
Claim processing is the main process where the customers are directly connected. In this case, delays or errors can significantly impact customer satisfaction. Machine learning in insurance has enabled the rise of Automated insurance claims, transforming how claims are submitted, assessed, and settled.
Technologies such as NLP in insurance allow systems to extract meaningful insights from unstructured data like claim forms, emails, and medical reports. Using NLP, insurers can automatically classify claims, validate information, and route cases to the appropriate departments.
In addition, Document intelligence enables automated verification of policy documents, invoices, and identity proofs, reducing manual intervention. For motor and property insurance, Image recognition models analyse photos or videos of damage to estimate repair costs and assess claim validity. Together, these technologies significantly reduce claim settlement time, lower operational costs, and improve customer experience.
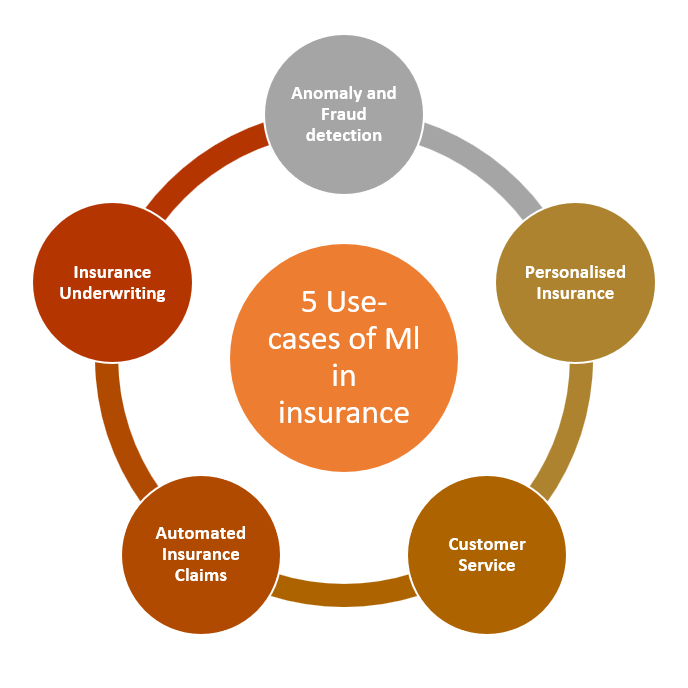
4. Personalised Insurance
In today’s world, personalisation has been one of the major requirements. Customers want personalised insurance as per their needs, lifestyle and risk potential. Machine learning in insurance makes personalised insurance a reality by enabling data-driven product customisation.
By analysing behavioural data, purchase history, and usage patterns, insurers can design flexible policies and dynamic premiums. This approach is particularly impactful in Private medical insurance, where machine learning helps personalise coverage based on health history, lifestyle choices, and preventive care data.
Additionally, Customer churn prediction models identify customers who are likely to switch providers. By proactively offering personalised discounts, benefits, or policy adjustments, insurers can improve retention and long-term customer value. Personalisation not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens brand loyalty in an increasingly competitive insurance market.
5. Customer Service
Customer service has evolved dramatically with the adoption of machine learning in insurance, especially through intelligent automation tools. Chatbot automation has become a key enabler of 24/7 customer support, handling routine queries such as policy details, claim status, and premium reminders.
These chatbots use machine learning and NLP to understand customer intent, provide accurate responses, and escalate complex issues to human agents when required. This reduces response times and operational costs while improving service consistency. Machine learning also supports Policy pricing queries by instantly generating personalised quotes based on customer data and risk profiles. As a result, customers enjoy faster interactions, while insurers achieve greater efficiency and scalability in customer support operations.
Evolution of the Insurance Industry Over the Years
The insurance industry has undergone a significant transformation over the decades. Initially, underwriting and Risk scoring were entirely manual, relying heavily on human judgment and limited historical data. Policy pricing was standardised, and claims processing was paper-intensive and time-consuming.
With the introduction of digital systems, insurers began using basic automation and rule-based models. However, these systems lacked flexibility and struggled with complex scenarios such as fraud detection and personalised insurance.
The adoption of machine learning in insurance and the evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) marked a turning point. Technologies like Predictive modelling, NLP in insurance, and chatbot automation enabled insurers to move from reactive decision-making to proactive, data-driven strategies. Today, insurance is evolving into a customer-centric, technology-driven industry where speed, accuracy, and personalisation define competitive advantage.
Drawbacks of ML in Insurance
Despite its benefits, machine learning in insurance comes with certain limitations:
Dependence on large, high-quality datasets can impact Predictive modelling accuracy
Lack of transparency in complex models may affect Risk scoring explainability
Bias in training data can influence Policy pricing and underwriting decisions
High implementation costs for Document intelligence and Image recognition systems
- Over-reliance on chatbot automation may reduce human empathy in customer service
Final Remarks
The adoption of machine learning in insurance has redefined how insurers assess risk, detect fraud, process claims, and engage with customers. From fraud detection using machine learning to personalised insurance offerings, the technology enables smarter, faster, and more customer-focused operations.
While challenges such as data quality, bias, and transparency remain, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks when machine learning is implemented responsibly. As the insurance industry continues to evolve, organisations that strategically invest in machine learning capabilities will be best positioned to deliver value, build trust, and stay competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.